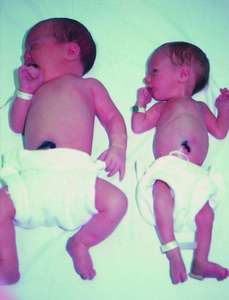
When you hear the term discordant twins, this means that the twins at birth show a distinct difference in size. Usually, the other twin’s weight is greater than 10%. This condition is common in identical twins but may also happen in fraternal twins.
To get properly oriented as to how this happens and how to manage this condition, there are essential things you need to know.
What Causes Twin Growth Discordance?
Twin growth discordance may happen in about 25% of twin pregnancies and can either be a weight discordance or size discordance. Weight discordance is a weight incongruence of more than 25% and is possibly associated with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) in the smaller twin.
Size discordance, on the other hand, is usually associated with anemia or can be a result of a twin-twin transfusion.

This condition is associated with a number of things like IUGR (intrauterine growth restriction) in the smaller twin, TTTS (twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome), or having a single umbilical artery (SUA) which is the absence of the right or left umbilical artery.
Discordance also happens when the placenta is unable to bring enough oxygen and nutrients to the growing baby. Other factors that influence this includes tobacco use, a viral infection, and if a mother does not have any prenatal care at all.
How are discordant twins diagnosed?
Growth discordance can be estimated by measuring the crown-rump length at or before 12 weeks of gestation. During the second and third trimesters, however, ultrasound measures are best used to estimate fetal weight and the degree of birth weight discordance.
Ultrasound examinations may be done in three different modalities:
- Two-dimensional (2D) Ultrasound Examinations will measure the fetal growth of both twins. It will also identify chronicity, as well as problems when it comes to the umbilical cord, TTT, and congenital abnormalities.
- The Doppler ultrasound will detect an abnormality when it comes to the patterns of blood flow in the fetal and placental circulation.
- A three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound is used to assess the placenta as to its surface, volume, and blood flow.
What should I expect in delivery?
The American Journal and Obstetrics & Gynecology states that there are three relevant combinations of fetal presentations when it comes to twin pregnancies in labor. These are vertex-vertex (both of the twins’ heads are down), vertex-nonvertex (one of twins’ head is down, while the other is in a breech position), and both non-vertex, where both twins are in breech.
The manner of delivery will be dependent on how twin A is presented. When twin A is vertex, it is possible to have a vaginal delivery, a planned cesarean section delivery, or combined (both vaginal and c-section).
A combined delivery is done when complications arise like a cord prolapse, placental abruption, fetal distress, or malpresentation of the second twin. Active management during the second stage of delivery involves maternal pushing, amniotomy (artificial rupture of membranes), and oxytocin administration.
In planned vaginal deliveries, standard protocols will be applied. This includes intravenous access, continuous fetal monitoring throughout the duration of labor, having sufficient nursing available, anesthesiology and pediatric support, ultrasound exam, and being ready to perform a cesarean delivery if needed.
What are the outcomes of a severe discordant fetal growth?
If the discrepancy is over 20%, there is a high possibility of the smaller twin to have adverse perinatal outcomes. This includes perinatal death (stillbirth), birth asphyxia, respiratory distress syndrome, neonatal infection, and birth trauma. In the case that the baby is born alive, there will be severe problems after birth.
The larger twin, on the other hand, may have a high risk of acute respiratory difficulty after birth. But aside from that, there will be fewer complications. In addition, they may be born prematurely. A C-section may also be induced to remove the twins from the mother’s womb before natural labor.
Twin pregnancies with discordant twins are at higher risk of prenatal complications and have a less favorable perinatal result. This is why early detection is most important for closer observation and well-timed delivery. Try to find out more about discordant fetal growth from your healthcare professional.






 Store
Store