Fraternal twins make up the majority of twins and account for 90% of multiple pregnancies. Unlike identical twins, this kind of twinning results in babies that have different sex and look different.
Read this in-depth information about how they are formed, how they differ from other twins and answers to your other questions.
What are Fraternal Twins?
They are dizygotic. They developed from two sets of sperm and egg that produces two babies that can be both girls, boys, or a combination.
They are independent. They do not share the same placenta and develop a separate amniotic sac.
How are Fraternal Twins Formed?
In a normal reproduction process, the sperm travels to meet the egg after sexual intercourse or in-vitro fertilization. If two eggs were released, two sperm will be able to fertilize the eggs that will eventually produce two genetically unique babies.
Twinning happens in several ways and produces higher order multiples depending on the number of eggs produced and the zygosity. This usually happens during hyperovulation, when a woman releases multiple eggs – mostly two.
In the case of these twins, two zygotes are produced with a genetic background like that of any two siblings born at different times. The only difference is that twins are conceived at the same time.
Do They Have the Same DNA?
No, they do not have the same DNA makeup. Just like any siblings, they share about 50% of their DNA and half each of their parent’s DNA. Each twin gets half of the mom’s egg and the half from dad’s sperm.
Can Fraternal Twins Look Identical?
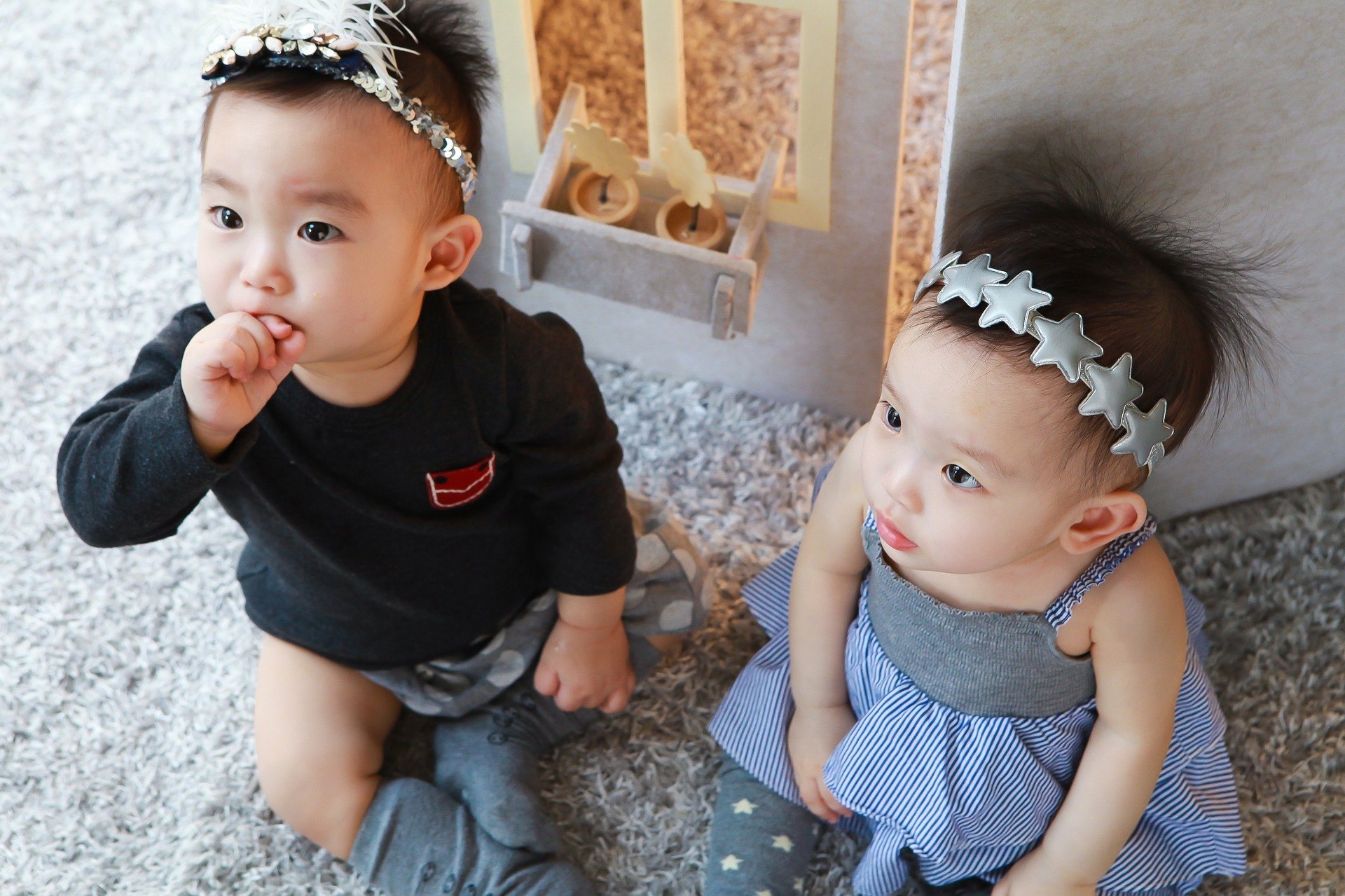

Since they do not share the same DNA, they also do not share the same chromosomes at the time of fertilization. However, they still share parts of their parents’ DNA so they may look alike, but not exactly identical.
Even twins that look alike can be distinguishable. Twins who were raised in the same home and were educated the same way, develop individual tastes and personalities.
Can They Be the Same Gender?
Yes, they can be both boys or both girls. Unlike identical twins who share the same sex chromosomes from a single fertilized zygote, they were produced by two separate zygotes that carry different sex chromosomes from their father.
Monozygotic twins, however, are always the same gender.
Doctors and health professionals usually identify if same-sex twins are identical or fraternal through other factors such as having shared placenta, chorion, and amniotic sac or through DNA testing. DNA testing is the surefire way to determine if twins are identical or fraternal.
Fraternal Twins Boy and Girl
Since conception happened for each egg, each egg carries the sex chromosome of the father. A girl has XX chromosomes while a boy has XY chromosomes. A boy-girl combination is the most common form of these kind of twins.
Chances of Having Fraternal Twins
The chances of having these twins are very much like with any kind of multiples. There are certain factors that increase the odds of a woman to conceive more than one baby at the same time.
- Assisted fertility treatments – This treatment includes IVF or In-Vitro Fertilization, fertility drugs, Intrauterine Insemination, and other advanced reproductive techniques. These treatments are becoming more and more common as well as more and more effective as years go by. The success rate of these treatments encourages women and couples to take this route. However, this increases the odds of conceiving multiples and the risks of pregnancy complications. This is because it encourages hyperovulation.
- Age of the Mother – It is believed that the older the woman gets, the harder it is for her to get pregnant. Although this is true, according to research, women over the age of 30 are more likely to conceive twins, if they ever get pregnant. This is because as women age, the follicle stimulating hormone level also increases.
- Weight – Women who are overweight also struggle with conception due to a lot of underlying medical conditions and the possible threat to their health and the baby’s health when they conceive. Some complications include high-blood pressure, diabetes, and many more.
- However, as ironic as it may sound, women who are overweight have higher levels of estrogen. This increased levels of estrogen stimulate the ovaries, which in turn produces more than one egg during ovulation.
- Family history – The odds of having twins in a family is hereditary. If a woman’s family has a history of twins and women who hyperovulate, the chances of producing twins are also increased.
- Race – Twinning also varies according to race. Studies show that some race produces more twins than others. This is especially true for Central-Africans and African-American women.
- Diet and nutrition – Some studies show that women who consume a huge amount of dairy products have a higher chance of conceiving twins.
- Height – Some research suggests that women who are taller have higher odds of having twins.
Are They Genetic?
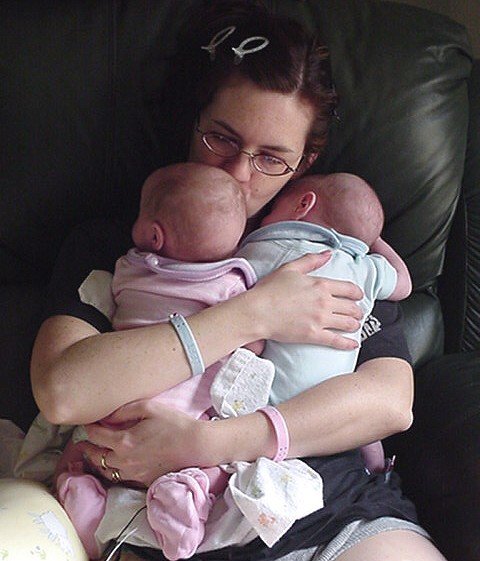

Yes, they can be. The factors above influence a woman’s odds of conceiving twins or multiples. Hyperovulation can be genetic, but it can result in multiple pregnancies of two, three, four, and higher multiples.
It just so happen that twins account for 90% of multiple pregnancies and having these twins is the most common type of twins.
Risks of Carrying Twins
- A woman carrying multiples is automatically considered as high-risk. The higher the number of fetuses in the womb, the greater the risks. This is because it poses a lot of potential complications for both mother and babies.
- The mother’s womb is fit for a single baby. If a twin or multiple pregnancies occur, complications such as Twin-to-Twin Transfusion Syndrome where twins do not get the equal amount of blood, oxygen, and nutrients that may affect the growth and development of babies in the womb, as well as cord entanglement.
- Birth defects are also a risk. This includes spina bifida, heart problems, defects of the digestive tract, and other neural tube defects that are due to reasons such as low amniotic fluid, TTTS, cord entanglement, and other reasons caused by unequal distribution of nutrition.
- For the mother, high-blood pressure, anemia, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and a higher chance of preterm labor and miscarriage. This is the reason why twins are born earlier than their singleton counterpart. If not, they are usually induced before 38 weeks and delivered via cesarean section.
- Then there is the risk of postpartum hemorrhage where the mother bleeds heavily after delivery due to the over-distended uterus and the large placental area.
Fraternal Twins in the Womb
Twins start to bond in the womb. They learn how to share nutrients and start to reach out to each other as they grow and develop. They grow in separate amniotic sacs and have separate placentas. They cannot physically reach out to each other, but they can feel each other in the womb and give each other some nudge.
Other Interesting Facts
- They may be conceived at different times by different fathers. When hyperovulation occurs, multiple eggs are released but it can happen a few days apart. So when one egg is released and the mother had sexual intercourse, that egg is fertilized and travels to implant in the uterus. As this happens, another egg can be released and fertilized by another sperm that may come from a different man.
- They do not have the same fingerprints. This is because fingerprint patterns are not affected by genetics. It forms as the fetuses develop in the womb, and the patterns are influenced by the environment in the womb.
- Twins develop a shared language as they grow up, and somehow feel each other’s emotions.
These are all the facts about how these twins are formed and other information regarding their genetic makeup and development. Fraternal twins are remarkably amazing.






 Store
Store